Canine Melanoma
Canine melanoma is the umbrella term for a group of melanocytic tumor subtypes that are so complex and diverse (yet distinct from each other)...
Quality of Life for Your Dog and You
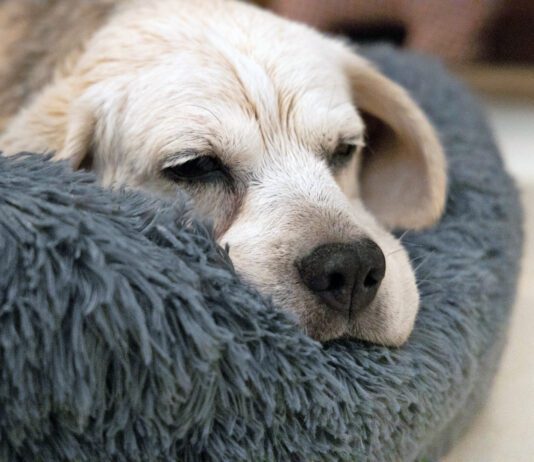
In August 2011 my friend Tory felt a couple of small lumps on the throat of her 13-year-old mixed-breed dog, Scout. Within a couple...
Going Long
Summer is for reading, yes? These long summer days are a perfect time to relax and enjoy a good, long read that improves your...
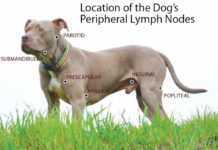
Canine Lymphoma: Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Lymphoma accounts for 7 to 24% of all canine cancers and approximately 85% of all the blood-based malignancies that occur, making it one of...
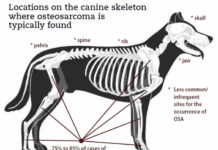
Osteosarcoma: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Osteosarcoma (OSA) has been found in every vertebrate class and has even been identified in dinosaur fossils, but it appears to be more prevalent...
About Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs
Mast cell tumors (MCTs) are the most common form of malignant skin cancer that occurs in dogs, accounting for about 14 to 21 percent...
A New Bone Cancer Vaccine for Dogs
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone tumor diagnosed in dogs, affecting an estimated 10,000 dogs each year in the U.S. alone. Too many owners are aware that this disease can be extremely aggressive with a poor prognosis.
Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs: Is It Always Cancer?
Mast cell tumors (MCTs) are one of the most frequent skin cancers seen in dogs. Mast cell tumors are the reason why careful monitoring of any skin growths is essential for maintaining a healthy canine. Any new masses on the skin should be evaluated by your veterinarian. In regards to MCTs, there are several predisposed breeds including Boxers, American Staffordshire terriers, and pit bulls.
Signs of Cancer in Dogs
Weight loss may be the first sign of cancer in dogs and can be easy to miss at home. As your dog ages, your veterinarian will likely recommend bloodwork, urinalysis, and other diagnostics. These can detect changes in organ function, possibly indicating cancer.
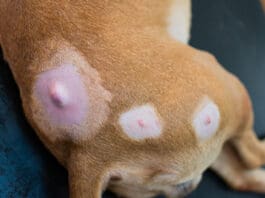
Hemangioma in Dogs
The cause of hemangiomas is idiopathic (unknown). These growths usually don't appear until at least middle age. Thin-skinned, light-colored breeds often experience hemangiomas. You'll most likely find a hemangioma on the dog's trunk or legs, especially hairless areas like the lower abdomen.
Reduce Your Dog’s Cancer Risks
Veterinary oncologists say that cancers in humans and in dogs are incredibly similar, in terms of growth and prognosis. That's good news for both species, as research of human or canine cancer may yield insight about and new treatments for this deadly disease. In addition, many of the tactics that reduce the incidence of cancer in humans, veterinary oncologists say, can be used by pet owners to reduce the chances that their dogs will develop the disease. Here are four things you can do to help prevent cancer in your dog.
Identifying Tumors on Your Dog
anyway. In this case